Mail Us: [email protected]
Call For Us: +86-13929487727
Two very common cutting processes in sheet metal processing are laser cutting and water jet cutting
Commonly Used Materials |
Cold-rolled sheet (SPCC), hot-rolled sheet (SPHC), galvanized sheet (SECC, SGCC), stainless steel (SUS304, SUS316), Aluminum sheet (Aluminum), Copper sheet (Copper), etc. |
Design key |
Bending radius: Usually not less than the thickness of the material. Hole/edge spacing: The distances between holes and between holes and edges need to take into account the mold and strength. Release slot: Prevents material tearing during bending. Tolerance: Clearly define the tolerance requirements for non-critical dimensions and critical dimensions. |
Forming |
Bending, Stamping, Roll Bending |
Connection and assembly |
Welding, Riveting, Threaded connection |
Finishing and Post-processing |
Deburring: Removes sharp burrs and sharp corners produced on the edges of cutting and stamping to ensure safety and usability. Smooth and burr-free edges with files, grinding machines and magnetic polishing machines Surface treatment: Powder coating, painting, electroplating, anodizing, etc. Parts with protective and aesthetically pleasing surfaces for spray lines and electroplating tanks Silk-screen Printing/laser Marking: Adds information such as labels, logos, and serial numbers to the surface of parts. |
I.Laser Cutting
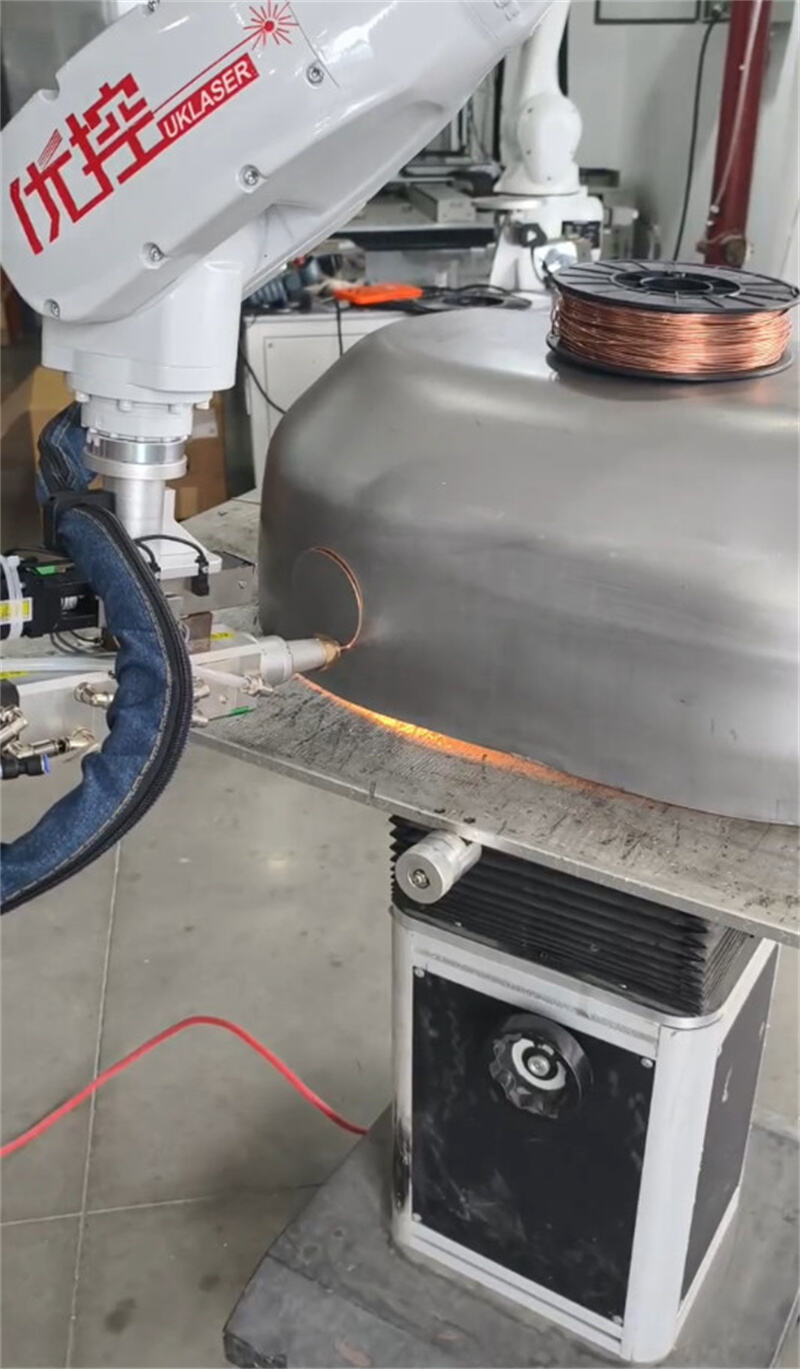
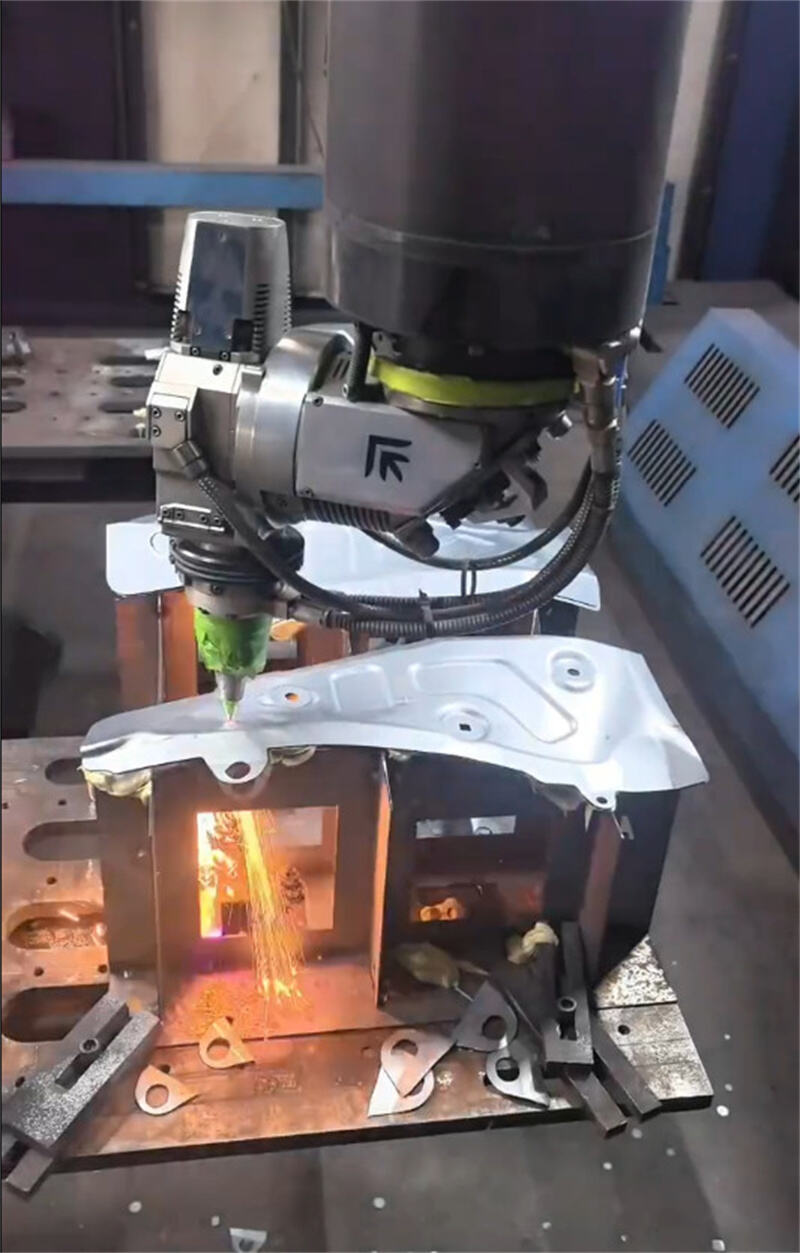
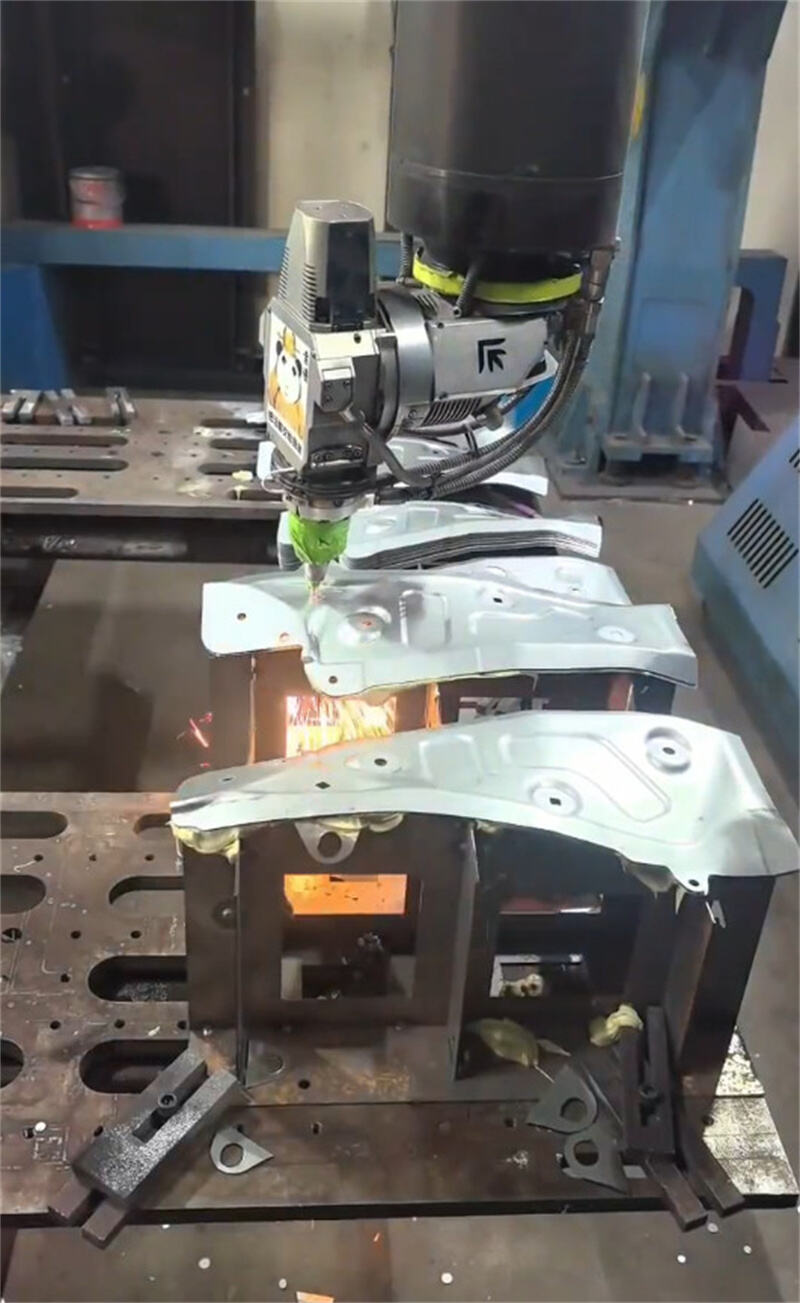
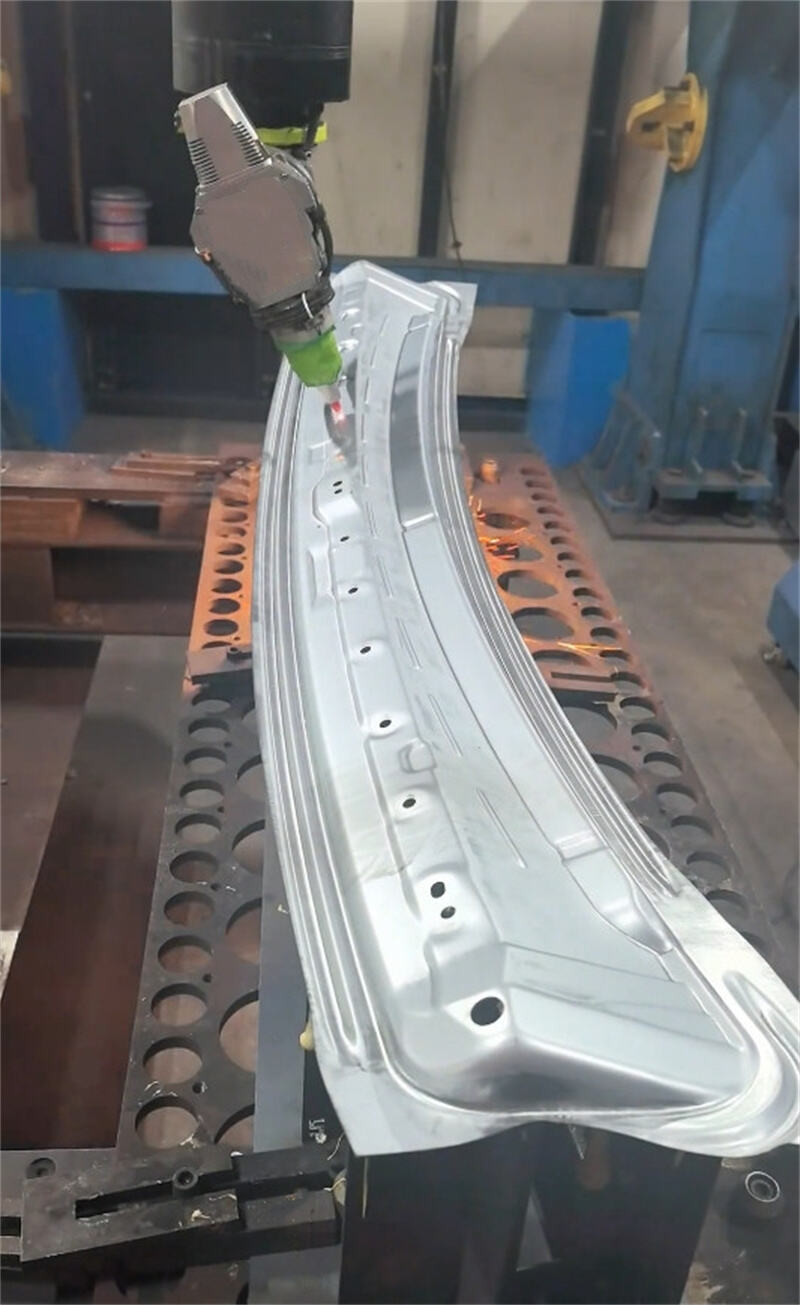




1.Process principle
Laser cutting uses a high-power-density laser beam focused by a lens as the heat source to irradiate the surface of the workpiece, rapidly heating, melting, vaporizing or reaching the ignition point of the material. At the same time, a high-speed gas flow coaxial with the beam is used to blow away the molten material, thus achieving the cutting.
2.The three core elements
High-energy laser beam, focusing optical system, auxiliary gas.
3.Typical applications
Chassis, cabinets, sheet metal enclosures.
Metal decorative pieces, artworks, signboard letters.
Automobile parts, bicycle frames.
Electrical parts, kitchenware.
II. Waterjet Cutting
1.Process principle
Water jet cutting, also known as water jet cutting, is divided into two types: pure water cutting and sand cutting.
① Pure water cutting: It uses an ultra-high pressure water pump (typically 300-600 mpa) to pressurize water, which then passes through tiny gemstone nozzles (with a diameter of 0.1-0.3mm) to form a high-speed jet (with a speed up to three times the speed of sound), relying on the kinetic energy of the water flow to erosion soft materials.
② Sand-adding cutting (sand-water mixed cutting) : Hard abrasives (such as garnet sand) are mixed into a pure water jet to form an abrasive water jet, which greatly enhances its cutting ability. It is like a "high-pressure water file", cutting hard materials through abrasive action.
III. Bending:
Bending is a cold working process in which external force is applied to metal sheet materials, profiles or tubes, causing them to undergo plastic deformation under the action of bending moment, thereby obtaining a predetermined Angle and shape. The core principle is to utilize the plasticity of the material to make it undergo permanent bending in a specific area (the bending line) without breaking.
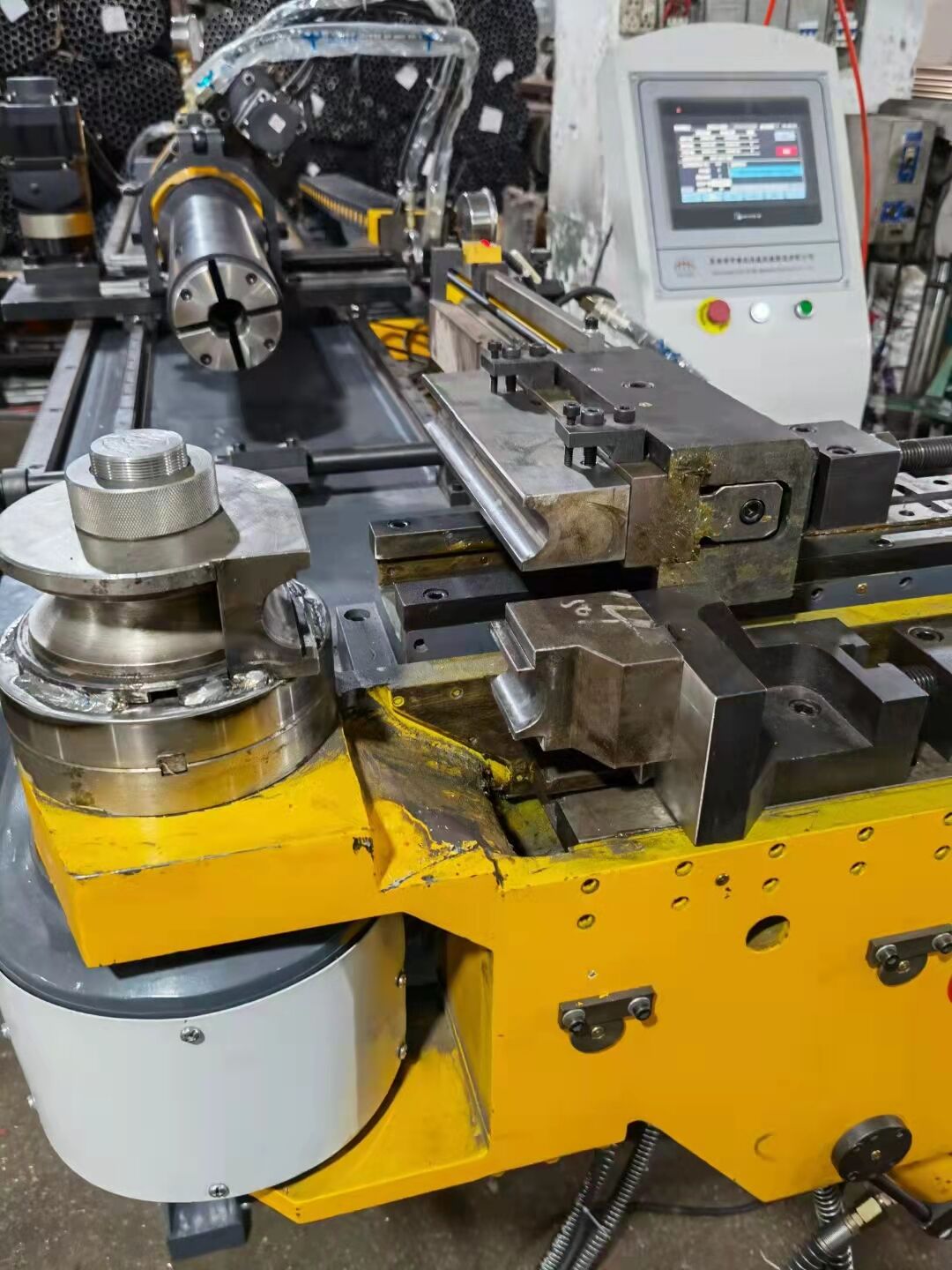

1.Main types/methods:
`Air bending: The most commonly used method. The upper die presses the sheet into the V-shaped opening of the lower die, but does not press it all the way down. The Angle is obtained by controlling the depth of the downward press. High flexibility, one set of molds can be folded at multiple angles.
`Bottom pressing bending/Calibration bending: The upper die completely presses the sheet metal into the bottom of the lower die, making it closely adhere to the inner wall of the die. It can effectively control springback with high precision, but it requires dedicated molds for each Angle and shape.
`Folding edge: First, perform a small-angle air bending, then flip the sheet and use the upper die to flatten or tighten the folded edge.
2.Main applications:
`Chassis and cabinets: Server cabinets, electrical control boxes, network equipment boxes.
`Sheet metal parts: brackets, hangers, enclosures, covers, ventilation ducts.
`Household appliances: refrigerator side panels, washing machine shells, oven panels.
`Architectural decoration: Elevator trim panels, metal ceilings, curtain wall components.
IV. Welding
Welding is a process method that combines two or more separate metal workpieces (of the same or different species) between atoms by heating, pressurizing, or both, thereby forming a firm and non-detachable joint.
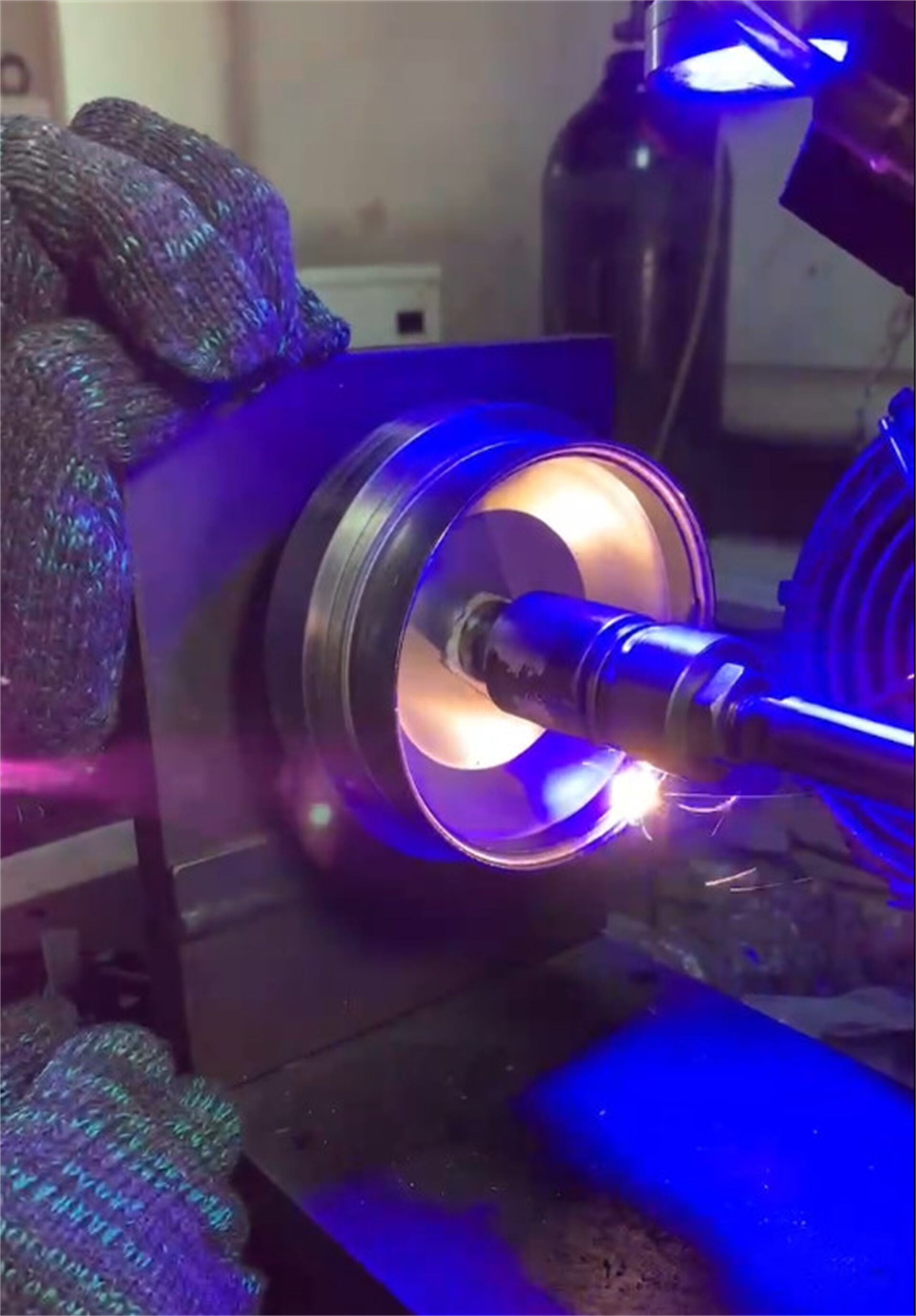
1.Main types/methods:
① Arc welding:
`Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) : The equipment is simple and the operation is flexible, making it suitable for outdoor work. However, it has relatively low efficiency and high requirements for the operator's skills.
`Inert gas metal arc welding (MIG/MAG) : It uses continuously fed welding wire as the electrode and is shielded by gas. MIG uses inert gases (such as Ar) to weld aluminum, stainless steel, etc. MAG welds carbon steel with reactive gases such as CO₂. High efficiency and the widest application.
`Tungsten inert gas welding (TIG) : Non-consumable tungsten electrodes are used, and additional filler wires are required. The protective gas is pure argon. The weld quality is extremely high, aesthetically pleasing, and suitable for thin plates, stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, etc. However, it has the highest requirements for the operator's skills and is slow.
② Resistance welding:
`Spot welding: By applying pressure to stacked metal plates with electrodes and passing electricity through them, the resistance heat causes local melting to form a weld point. Highly efficient, it is often used for the connection of a large number of thin plates in car bodies and home appliance shells.
③ High-energy beam welding:
`Laser welding: It uses a laser beam with high energy density as the heat source. Extremely high precision, small heat-affected zone, minimal deformation, and extremely fast speed. Suitable for automated production.
`Electron beam welding: It is carried out in a vacuum and has similar performance to laser welding, but the equipment is more expensive and complex.
2.Main applications:
`Manufacturing industry: Automobile bodies, ship hulls, pressure vessels, boilers, bridge steel structures.
`Construction industry: The steel frame of skyscrapers, oil and gas pipelines.
`Maintenance: Repair of equipment cracks and assembly of parts.
|
Laser |
Waterjet |
|
|
Working Principle |
High-energy heat source (melting/vaporization) |
Mechanical cold cutting (abrasive erosion) |
|
Heat Effect |
There is a heat-affected zone and it may deform |
No heat effect, cold cutting |
|
Material Range |
Metal is the main material, and reflective materials are difficult |
Almost all materials (metals, non-metals) |
|
Cutting Thickness |
Advantages of medium and thin plates (usually <25mm) |
Advantages of thick plates (up to 300mm+) |
|
Operating Cost |
The costs of electricity and gas are high |
The cost of abrasives and wear parts is high |
A: Yes, we are factory in Guangdong, China.
A:
Machining is 3-7 days for sample, 15-20 days for batch according to quantity;
Molding is 25 days for sample, 15-20 days for bulk.
A: Yes, we can, it need the sample fee, but can be refunded when place bulk order.
A: We offer flexible payment methods including bank transfer (TT), PayPal, Western Union, and Letters of Credit to facilitate secure global transactions. 30%-50% in advance, pay balance before shipping.
A: Yes, we can accommodate custom logos and packaging designs based on order quantities. Please discuss your specific needs with our sales team.
A: Yes, we support OEM/ODM customization based on your technical drawings, 2D/(PDF/CAD)3D(IGES/STEP).

Copyright © Dongguan Yuanji Technology Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved - Privacy Policy